 The COVID-19 pandemic continues to challenge schools, families, and communities. Thus, the new semester starts with many students (and teachers) preoccupied and anxious, and supporting students emotionally is a pre-requisite to teaching and learning. How do I teach my students when they are worried about the wellbeing of their family and themselves? What resources can I use to support the emotional needs of my students while ensuring they continue to learn? In this article we outline how to embed SEL in all aspects of teaching using as a resource and guidance The Standards of Practice of the NYS Next Generation Learning Standards. How do we define Social Emotional Learning? Social and Emotional Learning or SEL is defined by CASEL (1) as “… the process through which children and adults acquire and effectively apply the knowledge, attitudes, and skills necessary to understand and manage emotions, set and achieve positive goals, feel and show empathy for others, establish and maintain positive relationships, and make responsible decisions”. CASEL also identifies five SEL core competences: self-awareness, self-management, responsible decision-making, relationship skills and social awareness. 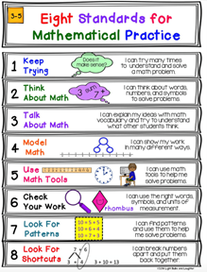 The NYS Standards of Practice are Aligned with the Social-Emotional Learning The NYS Next Generation Learning Standards include two types of standards: Content Standards, i.e. what students should know, care about and learn to do in a given grade, and the Standards of Practice which focus on are the competences, ways of thinking and behaviors that enable students the acquisition of content while building livelong learning practices. These practices such as persevering in solving a problem, asking questions or listening to understand are strongly connected to social-emotional learning (2). Standards for Mathematical Practice The first of the Standards for Mathematical Practice: Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them, aka “Keep Trying” encourages a student to question, try different perspectives, use concrete objects, and/or analyze a problem before jumping to quick solutions. It provides encouragement to think, discuss and collaborate within a defined context. The key words and colors used in this chart to describe the eight standards make them inviting and can lower a student’s anxiety to learning math. When applying the Standards for Mathematical Practice students use their visual, language and cognitive competences along with mathematical content making them feel empowered and therefore, more eager to learn the concepts and operations.  Science and Engineering Practices (Dimension 1) The New York State P-12 Science Learning Standards are based on the Framework for K–12 Science Education developed by the National Research Council and the Next Generation Science Standards. They integrate three key dimensions: the Practices, the Disciplinary Core Ideas and Crosscutting Concepts. The Science and Engineering Practices model the inquiry process used by scientists. These practices such as asking questions and/or engaging in argument using evidence encourage conversations, the exchange of idea and inquiry which are essential to the discovery process. In today’s environment, having conversations based on evidence can help students overcome some of their fears and immerse themselves in the learning process.  Life – Long Practices of Readers and Writers Students are also authors and writers, and when they read a new text, they want to figure out the meaning of the words in a paragraph, re-read it to understand the story in front of them, explain it orally, think about it and make predictions about possible outcomes. Authors and writers also look for patterns, so they can write a story summary and check their work. When we teach students as authors and writers, and when they practice these competences in a inductive manner, they become empowering, help them feel better about themselves and their own capabilities, thus ready to continue learning. The revised NYS Next Generation Learning Standards place special emphasis on these Standards of Practice because it supports the development of Social Emotional Learning in the context of specific content areas. At the school level, it is a tool that provides guidance and consistency while encouraging collaboration among teachers across grades and subjects.
0 Comments
Your comment will be posted after it is approved.
Leave a Reply. |
Archives
January 2024
Categories
All
|
